How does CDN DNS work?
Content Delivery Networks have been around since the early 90s, but only recently have they started making big waves for smaller companies and colossal corporations alike. Content delivery platforms are an elemental component of internet infrastructure. Without CDN hosting, thousands of websites are bound to load slow–not to mention crash and go offline. That being said, if you’re new to the technology, we’re here to answer one of the most searched questions online today: how does CDN DNS work?
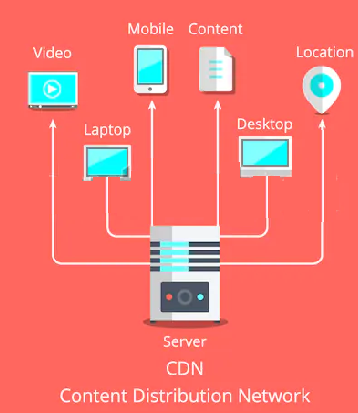
For this article, we’ll talk about CDN hosting, examine the variables that make the best CDN, and why your website needs it to survive the new digital era.
how does DNS work?
Every time a web browser makes a resource request, a DNS request always comes first. This quick process is a lot like looking up a contact on your mobile’s contact list: an IP address is expected once your browser of choice provides the domain name. The browser can then directly reach out to the webserver using the IP address. Smaller blogs and websites generally have corresponding domain names that have one IP address. On the other hand, larger web applications may still have one domain but utilize multiple IP addresses.
In other words, the answer to “how does CDN DNS work?” is simple: every time you play a video, enlarge a photo, open a new link, or download a file, you’re device is making a request through the internet. If your website is supported by CDN hosting, your web content is consumed much faster by your international users. If it doesn’t, the request they make travels to wherever your web host origin is.
For example, when your site is hosted by an origin server in Chicago, the request of all your global site visitors make still has to travel to Chicago. If your primary market is from Michigan or Ohio, that’s mostly fine. Your site users from these states enjoy quality browsing. But when you have users from Tokyo or New Zealand, you can already be sure your site will load a little later than desired.
How does DNS work with the best CDN?
It’s easy to get carried away with big CDN hosting companies. After all, that’s exactly what branding teaches us: the best CDN has to be the biggest. Right? Wrong. It’s important to note that every website is unique and businesses don’t and shouldn’t have the same version of what the best CDN is. What works for you may not exactly work for others and vice versa.
For instance, one of the most important things to look at when signing up with a provider is their distribution reach. How many Points of Presence (PoPs) do they have and do they have data centers in the regions and countries that matter to your business the most? These things are crucial because this is exactly what helps reduce latency. Now, it’s a given that bigger CDN companies have a whole lot of locations, but there are other questions we need to ask, too:
- How justifiable are these rates in the CDN market today?
- Are there other CDN providers that have the same PoPs my business needs the most but at a cheaper price?
The best CDN only becomes the best when your unique website and business needs are catered to.
Does my website need CDN hosting?
More than half of the internet that exists is being managed by CDN hosting companies. Although that’s a startling fraction, it also doesn’t immediately mean your website should be part of that half. When deciding whether or not it’s time to sign up with a provider, remember the answer to how does CDN DNS work?
CDNs exist to efficiently relay your web content to your users who are distant from wherever your web host origin is. If your site exists to serve a distinct market that’s relatively close to your web host origin, there’s a high chance you don’t need a CDN anymore. However, if you have a growing audience from different parts of the world, then getting a CDN is a smart idea. Not only will you be afforded easier access to a wider audience, but you’ll also naturally draw in more converts, too. Prime examples of digital empires that benefit greatly from CDNs are video-streaming websites, social media companies, journalism agencies and internet publications, and the eCommerce industry. Without CDNs, their digital havens would take forever to load and segmenting global audiences would be difficult.
The rewards quick-loading websites can reap are tremendous and should never be overlooked.
Everything you need to know about https-ssltls